Rivulet pouring into Rio Santa Barbara upper watershed (photo by J. F. Matthews, July 2010).

Rio Santa Barbara upper watershed mature forest (photo by J. F. Matthews, July 2012).

Flora on Rio Santa Barbara upper watershed (photo by J. F. Matthews, July 2010)

Flora on Rio Santa Barbara upper watershed (photo by J. F. Matthews, July 2010).

Flora on Rio Santa Barbara upper watershed (photo by J. F. Matthews, July 2010).

The house on 17 irrigated acres from the Rio Santa Barbara Acequia de San Juan Nepomoseno del Llano. Water rights since 1789 (photograph and data by Taos Properties).
(This new post derives from my previous post, “Not mine, not yours, but ours: Penasco Upper Llano acequias,” October 2011.)
From Amarillo, Texas, I drove to northern New Mexico in 1968. I traveled by way of Las Vegas, Mora, and Penasco, making camp along the upper watershed of the Rio Santa Barbara for a few days. I vividly remember a man plowing his field with horses near Mora and the narrow strips of farm land that bordered rivers and irrigation ditches. The narrow strips of irrigated land not only reflected a precise lay of the land by residents and survey crews, but the long lots reflected a community, a meshing of rural families alongside a water greenbelt. In later anthropological field trips, I took my Amarillo College students by the Pecos River irrigated plots along State Highway 3 that ran from Interstate 40 to Interstate 25 between Santa Rosa and the Pecos Pueblo. (Click to see Google map of the Pecos River plots.)
The system of irrigation is called acequia, referring both to the irrigation ditch and the association of members organized around it.
I have never owned land in New Mexico, but if I did I would buy a parcel of land that had water rights to an acequia, a system that stretches back in time to Native American communities before the arrival of the Spanish who brought laws respecting community water rights (riparian rights). Having land that possesses an acequia, one gains entry into a community that cleans, rebuilds and nourishes the ditches and, further, is granted rights to meet in a democratic association to discuss apportioning water and policies affecting owners that border the irrigation ditch.
Several weeks ago, I came across a piece of property near Penasco that if I could sell my ranchito, I would buy and move my horses and equipment post haste to Penasco Upper Llano. See the following Google map: This is the map-image of the Penasco Upper Llano property and other long lots of community property.
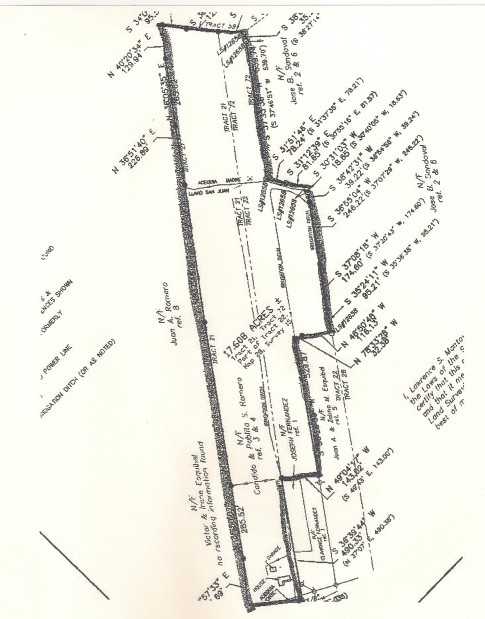
This particular piece of property with the house pictured above is located in the high country between Taos and Santa Fe and can produce 700 bales of hay a year. The water rights go back to 1789, the year that the United States inaugurated its first president, George Washington. The surveyor’s plat looks like this:
Several good books and narratives have been written about the acequia culture. Stanley Crawford in his work, Mayordomo: Chronicle of an Acequia in Northern New Mexico (1988), writes of the acequia culture:
There are few other civic institutions left in this country in which members have as much control over an important aspect of their lives; relatively autonomous, in theory democratic, the thousand acequias form a cultural web of almost microscopic strands and filaments that have held a culture and landscape in place for hundreds of years….
Ditch-cleanings are all very much the same, and in this they often feel more like ritual than work. The crew varies from year to year: a couple of old men don’t turn up each year, a couple of boys barely able to handle a shovel, fifteen- and sixteen-year-olds, take their places; the weather is better or worse than some vague notion of what is usual, mayordomos come and go and some are responsible and fair, others vindictive, punitive, almost military, others are lazy and heedless of the needs of the ditch; and the crew can be a good-natured, hard-working creature, or sullen and complaining and evasive, qualities perhaps dictated by the amount of pride or fear circulating through the hearts of both those in charge and those doing the actual digging….
Buddy Manzanares who, on one of my last perfunctory inspection tours half an hour from the end of the spring digging, calls on me to admire a meticulously dug out and cleaned up tarea [a grave-size chunk of the ditch], with the banks cleaned of grass and squared neatly where they end in the bottom of the smoothly shoveled-out channel….This man knows how to make this small thing, this chore, into more than we commonly imagine, and what can be more important to know in this life, than just that.
Mayordomo, pp. 176, 224, 228-29.
The deep thing about acequia that attracts me is the ready-made community that circulates around water rights that nourish subsistence crops and the growth of hay. The isolation of many Texas ranches and the people that tend them and steward their animals is not good; in fact, it diminishes the rancher to a coarse individuality that thins the possibilities of human endeavors, insinuates a obsessive pecuniary attitude about the land and narrows civic — read unselfish — behavior to the mere casting of a vote once or twice a year for politicians.
There are western ranching communities that transcend these deficiencies, I grant you, but the tendency has been to sell out or buy more land, thus expelling more people from the agrarian way of life. I have experienced this and have witnessed the deleterious affect upon my family.
I do not romanticize the acequia culture because it is a human community and there will be conflict and law suits. Nonetheless, there exists an association of men and women meeting about water and how to nourish their livestock, beans, alfalfa, corn, tomatoes, okra, flowers, lawns, chilis, vineyards, peaches, plums, apricots, coastal bermuda, roses, trees, and every other conceivable plant needing water that flourishes from the earth. Having an acequia culture forces upon us the lesson about sharing in real, material ways that no desk-bound, box-bound person will ever learn. The basic premise is: water is limited, we all need it, how will we share it? And, how are we going to keep it coming down the ditch? The answer: let’s talk about it, let’s vote on it, let’s implement our decision, and we will meet again.
Like so many other things in life, the ditch is more than a ditch. The acequia and the water is not mine, not yours, but ours. Water is life, and in this case, Life is a Ditch.

Acequia near Vadito, New Mexico, (Vadito II, oil by Eric Andrews, Taos, personal collection of J. Matthews).
______________________________
Notes, corrections and additions:
The language keyboard for Spanish and diacritical markings frustrates me. Hence, the Spanish diacritical markings for “Penasco” are missing, although about every 20 times, I can get the tilde above the “n” in Penasco. If anyone has any suggestions within the WordPress format to easily apply diacritical markings to writing, please comment or drop me an email at matthewsranch@msn.com. I am intent upon using proper markings, but I am not going to spend ten minutes every time I need a tilde to paste it on. Can Windows Vista do anything right? Of course they can, but you have to update your browser every five minutes. And, then restart.